
Icd 10 code closed supracondylar fracture elbow skin#
It gives damaged skin time to improve before surgery to fix the fracture and may reduce the risk of infection.
The external fixator acts as a frame to help hold the elbow in a good position until a second surgery can be performed. The pins project out of the skin and are attached to carbon fiber bars outside the skin. In this operation, the doctor makes small incisions into the skin and inserts metal pins through the bones. For severe open fractures, your doctor may apply an external fixator to hold the bones in place until a second surgery can take place. In some cases, however, open fractures will require more than one surgery. The bone will typically be repaired during the same surgery. During surgery, the cuts from the injury and the surfaces of the broken bone are thoroughly cleaned out. Patient are given antibiotics by vein (intravenous) in the emergency room, and may receive a tetanus shot. Pieces of bone have punctured the skin (open fracture)īecause of the increased risk of infection, open fractures are scheduled for surgery as soon as possible, usually within hours.The bones have moved out of place (displaced fracture).Surgery is usually required for distal humerus fractures in which: (Right) An elastic bandage is applied to help keep the splint in place. (Left) The doctor will apply a splint that runs from near your shoulder all the way to your hand. If the fracture shifts out of position during this time, you may need surgery to put the bones back together. Splints are typically worn for 6 weeks before supervised motion is started. During the healing process, your doctor will take frequent x-rays to make sure the bone has not shifted out of place. Your doctor will apply a splint or sling to hold the elbow in place during healing. For example, patients with severe osteoporosis or other medical conditions may not be able to tolerate surgery. It may also be recommended for patients who are at higher risk for surgical complications. Nonsurgical treatment may be recommended for stable fractures in which the pieces of bone are not out of place (displaced). Some distal humerus fractures can be treated without an operation, but this is rare. Whether or not your fracture requires surgery will then be determined. Applying ice to reduce pain and swelling.
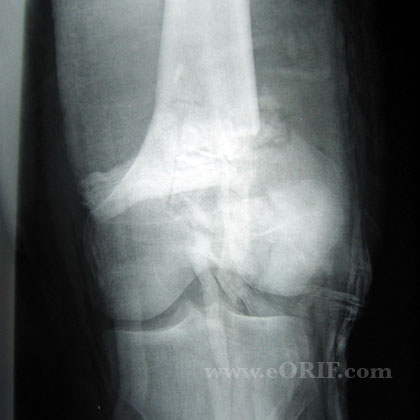
While you are in the emergency room, your doctor will apply a splint (like a cast) to your elbow and give you a sling to help keep your elbow in position. Your doctor will order x-rays of your elbow to help diagnose your fracture.ĭepending on your symptoms, your doctor may also order x-rays of your upper arm, forearm, shoulder, wrist, and/or hand to ensure that you do not have any other injuries. X-rays provide images of dense structures, such as bone. This can result in weakness and numbness in the ring and small fingers.Īlthough you may have pain only at the elbow, your doctor may also examine your shoulder, upper arm, forearm, wrist, and hand to ensure that you do not have any other injuries. In some cases, the ulnar nerve may be injured at the same time the fracture occurs. Check to see that you can move your fingers and wrist, and can feel things with your fingers.Check your pulse at the wrist to ensure that there is good blood flow to your hand and fingers.This could indicate other broken bones or injuries, such as a dislocated elbow. Palpate (feel) all around your elbow to determine if there are any other areas of tenderness.In severe fractures, bone fragments can break through the skin, increasing the risk of infection. Check your skin for cuts and lacerations.He or she will then examine your elbow to determine the extent of the injury. Your doctor will talk with you about your medical history and general health and ask about your symptoms. Most patients with distal humerus fractures will go to an urgent care center or emergency room for initial treatment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
