

Sol: The given plate is symmetrical about the y-y axis, therefore \ = 150 mm. Because r is the distance to the axis of rotation from each piece of mass that makes up the object, the moment of inertia for any object depends on the chosen axis. To find \, we have to divide the whole Figure into standard areas.Įxample: Find the moment of inertia of a plate with a circular hole about its centroidal x axis as shown in Fig.8. We defined the moment of inertia I of an object to be I i mir2 i for all the point masses that make up the object. The centroid is located symbolically at xC.yc Find (1) xC.圜, the location of the centroids x and y coordinate (2) IxC, the area moment of inertia about the. The second moment of area is a measure of the efficiency of a cross-sectional.
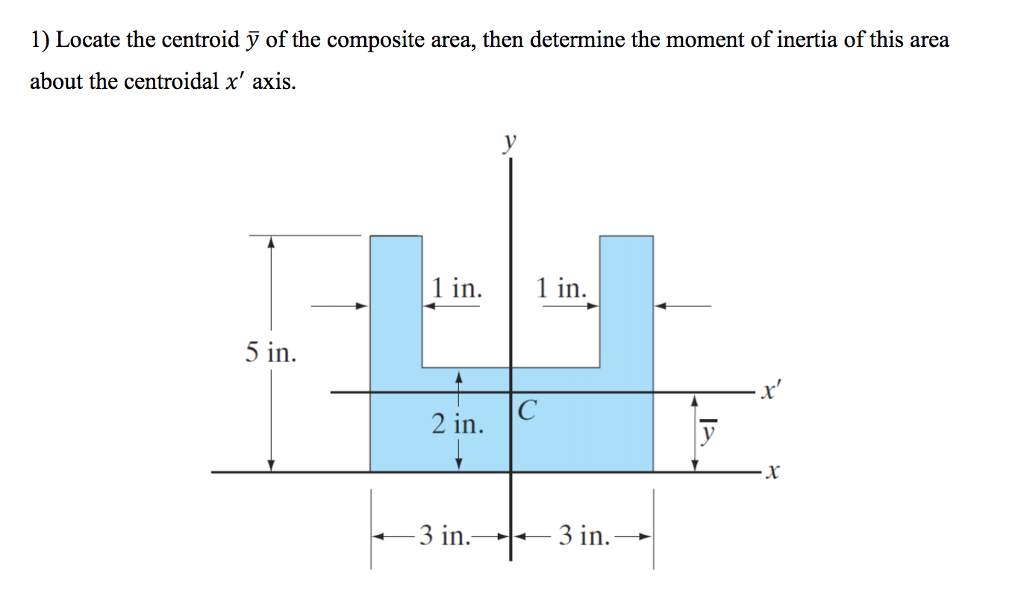
Sol: The given I-section is symmetrical about the y-y axis, therefore, The second moment of area is also known as the moment of inertia of a shape. = + Įxample: Determine the moment of inertia about the horizontal axis passing through the centroid of the section as shown in Fig.7. Moment of Inertia is the integration of the square of the distance of the centroid and the del area along the whole area of the structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
